Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung affecting primarily the microscopic air sacs known as alveoli. It is usually caused by infection involving viruses or bacteria and less commonly caused by other microorganisms, drugs or other conditions such as autoimmune diseases.
Typical signs and symptoms of pneumonia include cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. Diagnostic tools include x-rays and a culture of the sputum. Vaccines to prevent certain types of pneumonia are available. Treatment depends on the underlying cause. Pneumonia presumed to be bacterial is treated with antibiotics. If the pneumonia is severe, the affected person is hospitalized.
The images below are of a human lung infected with viral pneumonia and were captured with the RB30 clinical lab microscope using the HDCAM4 high definition microscopy camera.
Typical signs and symptoms of pneumonia include cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. Diagnostic tools include x-rays and a culture of the sputum. Vaccines to prevent certain types of pneumonia are available. Treatment depends on the underlying cause. Pneumonia presumed to be bacterial is treated with antibiotics. If the pneumonia is severe, the affected person is hospitalized.
The images below are of a human lung infected with viral pneumonia and were captured with the RB30 clinical lab microscope using the HDCAM4 high definition microscopy camera.
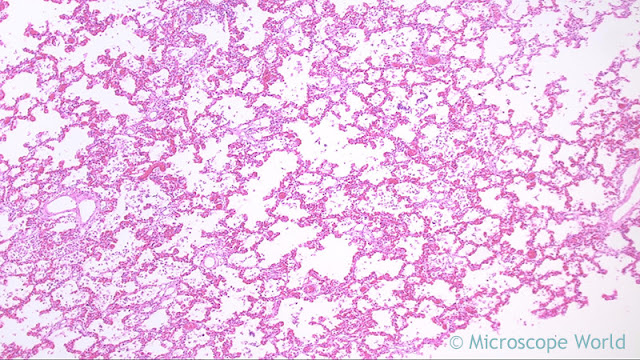 |
| Lung infected with viral pneumonia under the microscope at 40x. |
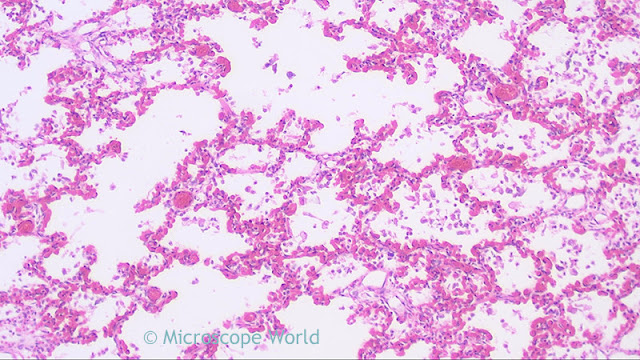 |
| Lung infected with viral pneumonia under the microscope at 100x. |
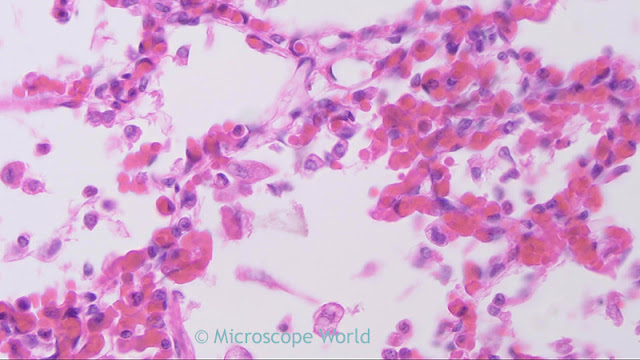 |
| Lung infected with viral pneumonia under the microscope at 400x. |
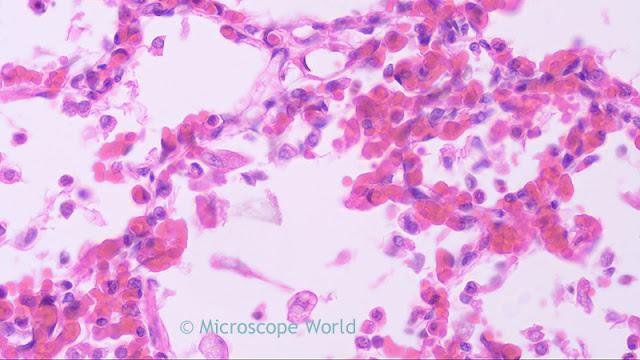 |
| Lung infected with viral pneumonia under the microscope at 400x using a Semi Plan Apochromat Fluor objective. |