Carcinoma of the Prostate, also known as
Prostate Cancer, is the development of cancer in the prostsate. The prostate is a walnut sized gland in the male reproductive system. Most prostate cancers grow slowly, but the cancer cells may spread to other parts of the body, in particular the bones and lymph nodes.
Late stages of prostate cancer can cause symptoms such as difficulty urinating, blood in the urine, or pelvis or back pain while urinating. Feeling tired is another common symptom as the cancer causes low levels of red blood cells.
Prostate cancer is diagnosed by a biopsy. The images below of prostate cancer were captured using the
RB30 biological lab microscope and the
DCM3 microscope camera (3 megapixels).
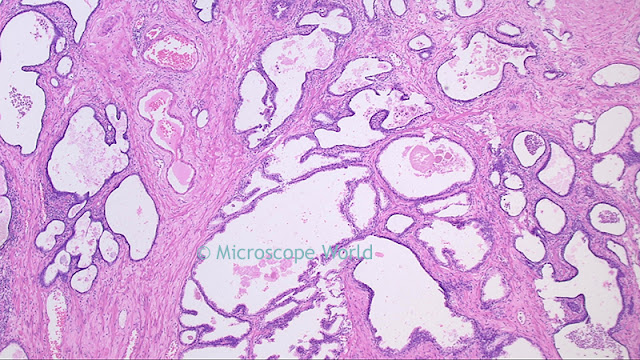
![Prostate cancer image under the microscope. Microscopy image of prostate cancer at 40x.]() |
| Prostate cancer under the microscope at 40x magnification. |
About ninety-nine percent of prostate cancer cases occur in men over the age of fifty. Diets high in processed meat, red meat or milk products and low in vegetables can increase prostate cancer risk.
![Prostate cancer under the microscope. Lab microscope image of prostate cancer at 40x from MicroscopeWorld.com.]() |
| Prostate cancer under the microscope at 100x magnification. |
Prostate cancer screening is controversial because prostate-specific antigen (PSA) testing increases cancer detection but does not decrease mortality. PSA testing sometimes results in over-diagnosis and over-treatment as most cancers diagnosed would remain asymptomatic.
![Microscopeworld.com image of prostate cancer at 400x. Prostate cancer image from MicroscopeWorld.com captured at 400x.]() |
| Prostate cancer under the microscope at 400x magnification. |
The five-year survival rate for prostate cancer in the United States is ninety-nine percent.
You can learn more about prostate cancer
here.