A
microscope reticule (also known as a reticle), is a small piece of glass inserted into the microscope eyepiece for counting or making measurements. This small circular glass disc has an image imprinted on it such as a grid, protractor or ruler. There are a number of different types of microscopy reticules, and each is explained briefly below. Click on the link in order to view a wide variety of reticules in each category.
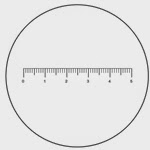
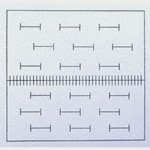
![Microscope ruler reticle Microscope ruler reticule]()
Microscope
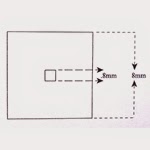
ruler reticles are the most popular type of reticule used and are ideal for making basic measurements. Available in both mm and inches, the ruler reticules can be NIST certified for precise measuring that meets certifiable standards.
![Microscope grid reticule Microscopy grid reticle.]()
Microscope
grid reticles are frequently used for counting or measuring cells or particles. Measuring particles and cells is made easier, especially if the required task is a pass/fail task. By knowing the size of the grid and whether a particle or cell fits within that grid can make the job of viewing multiple samples at one time more efficient and timely.
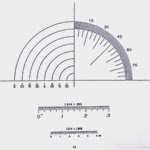
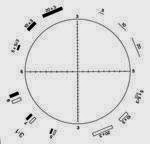
![Microscope comparator reticule Microscopy comparator reticle]()
Microscope
comparator reticles are typically used for measuring angles. Similar to a protractor, the comparator reticle is available with or without a ruler printed beneath it.
![Crossed-scale reticule Microscopy crossed scale reticle.]()
Microscope
crossed scale reticles are similar to ruler reticles, but have rulers on each of the four axis points. These reticles are useful when needed to measure in several directions from a center point.
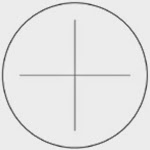
![Microscope cross line reticle. Microscopy cross line reticules.]()
Microscope
cross line reticles typically do not have measuring features on them. These microscopy reticles are cross lines, or cross lines with multiple angles, such as a pie.
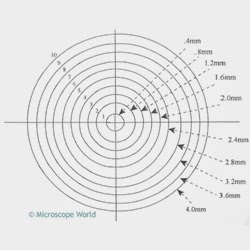
![Microscope concentric circle reticle. Microscopy concentric circle reticules.]()
Microscope
concentric circle reticles are used to measure tolerances from a central point. By using concentric circles, the distance between each circle on the point is a known distance and making measurements of tolerances is much easier.
![Microscope grain sizing reticule Microscope grain sizing reticle.]()
Microscope
grain sizing reticles are used for measuring twine, austenite, carbide, brass, and copper. Additionally grain sizing reticles that meet ASTM E112 grain counting standards, Methods ASTM E-45 A, D and E method, and ASTM C method are reticles that meet specific industry standards.
![Microscope whipple reticules Microscopy whipple reticles.]()
Microscope
whipple reticles have a grid system that usually contains a grid within the main grid. Whipple reticles are intended to enable the measurement of smaller specimen features such as pigment dispersions, colloidal particles, dust, and bacteria.
![Point array reticules. Microscope point array reticles and point cross array reticles.]()
Microscope
point dot array and point cross array reticles are used for counting.
![Microscope Merz reticules Microscopy Merz reticles.]()
Microscope
Merz Reticles are used to estimate the three dimensional surface areas or the surface density of a component in a given volume, when the component does not have a random orientation. It comprises a test system with parallel curved lines used for measuring the intersection of points.
![Microscope pinwheel reticule Microscopy pinwheel reticles.]()
Microscope
pinwheel reticles are much like the name - a pinwheel with a measuring ruler on each leg of the pinwheel.
![Microscope specialized counting reticules. Microscopy counting reticles.]()
Microscope
counting reticles include everything from Birnell Scale, Dargie reticle, dirt estimation reticle, Fairs Analysis reticle, Howard mold counting reticle, hole gage reticles, milk smear, Reticulyte counting reticles, Walton & Beckett reticles, Patterson globe reticles, IMA/USP counting reticles, Miller Disc square reticles, Weibel reticles and Porton Counting reticles.
![Microscope square reticules Microscope square reticles.]()
Microscope
square reticles and concentric square reticles are commonly used to measure set dimensions.
Once you have your microscope reticle,
read this page to find information about how to accurately measure with your reticle.
If you are looking for a particular type of microscope reticle and don't see mention of it on this page, please
contact Microscope World, as we carry a number of reticles that are not listed here, as well as custom microscopy reticles.