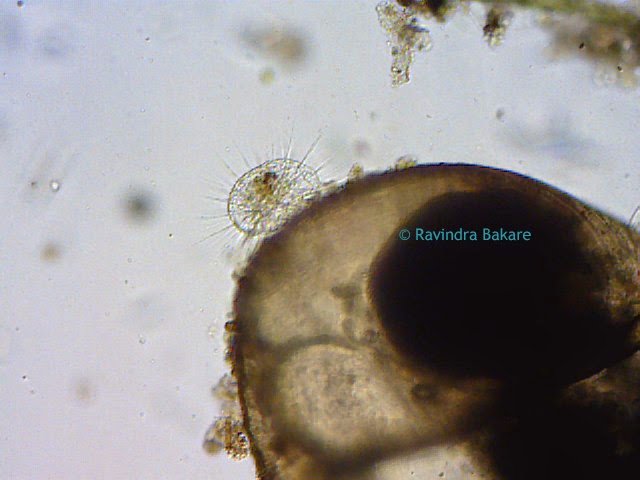
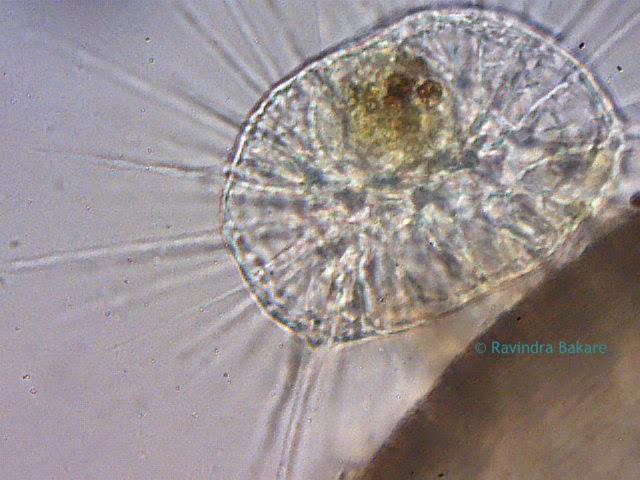
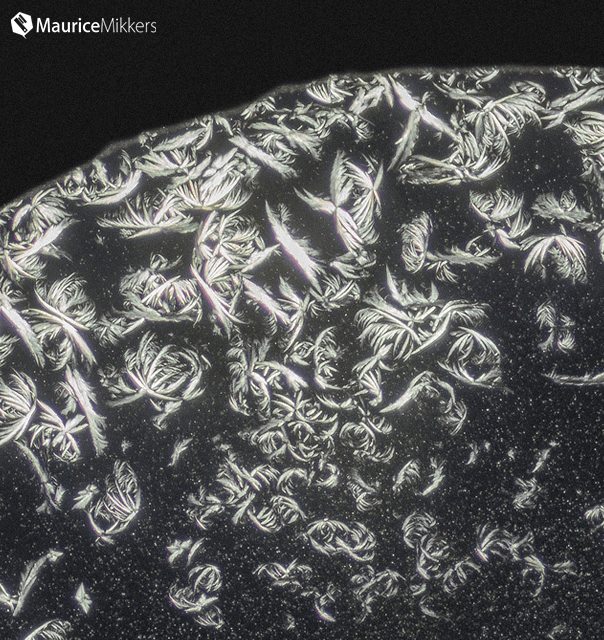
Arcella Vulgaris is a Testate Amoeba that has loose pseudopodia protruding out of the pseudochitin shell. This video shows the Arcella Vulgaris producing Carbon Dioxide vesicles to create buoyancy. The test (or shell on sea urchins and microorganisms) is for protection and secreted by the animal itself. Testate amoeba are amoeba that have an umbrella shaped hard covering.
Arcella Vulgaris lives among water weeds and feeds on bacteria. The video also shows another variety of Arcella sp. which is transparent and the Amoeba inside can clearly be seen.
In the video captured by Ravindra Bakare, Associate Professor of Zoology at Kisan Veer Mahavidyalaya in Wai Dist Satara, Maharashtra, India, stagnant pond water was collected near the University and placed under a biological microscope. Bakare works for the fresh water protozoan diversity around Wai and captured this Arcella Vulgaris video under the microscope by using a 2 megapixel eyepiece camera at 45x magnification. Microscope World is grateful for Ravindra Bakare's hard work in capturing this video and for sharing it with microscopy enthusiasts!
Arcella Vulgaris lives among water weeds and feeds on bacteria. The video also shows another variety of Arcella sp. which is transparent and the Amoeba inside can clearly be seen.
In the video captured by Ravindra Bakare, Associate Professor of Zoology at Kisan Veer Mahavidyalaya in Wai Dist Satara, Maharashtra, India, stagnant pond water was collected near the University and placed under a biological microscope. Bakare works for the fresh water protozoan diversity around Wai and captured this Arcella Vulgaris video under the microscope by using a 2 megapixel eyepiece camera at 45x magnification. Microscope World is grateful for Ravindra Bakare's hard work in capturing this video and for sharing it with microscopy enthusiasts!