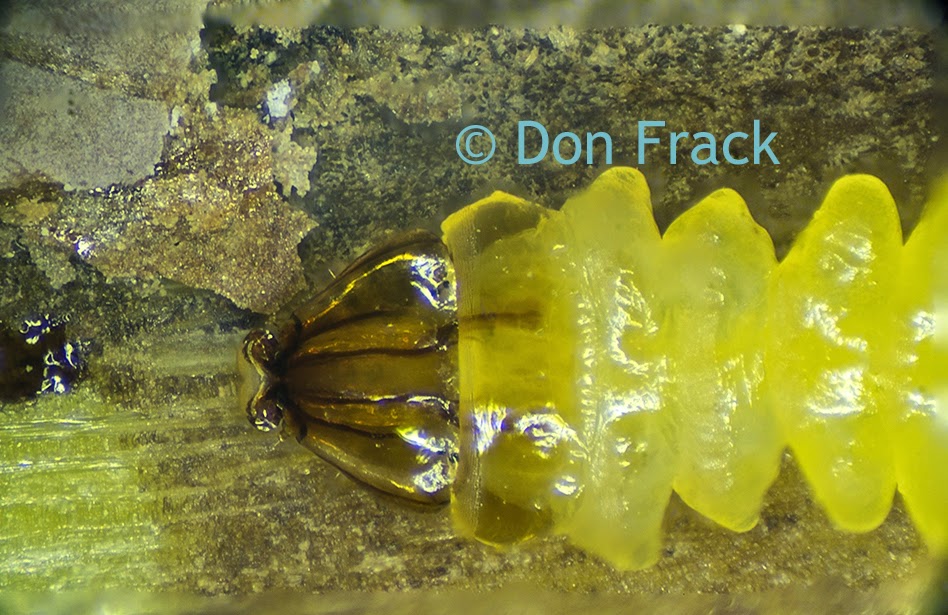
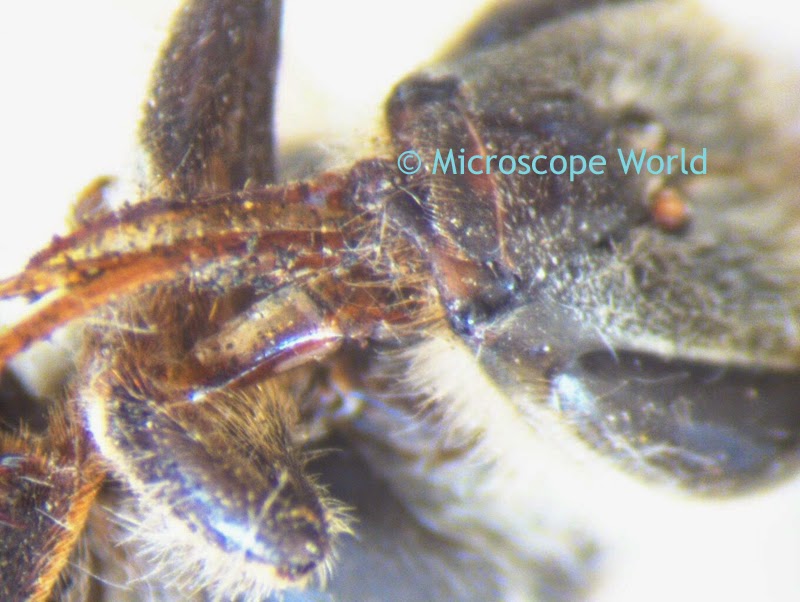
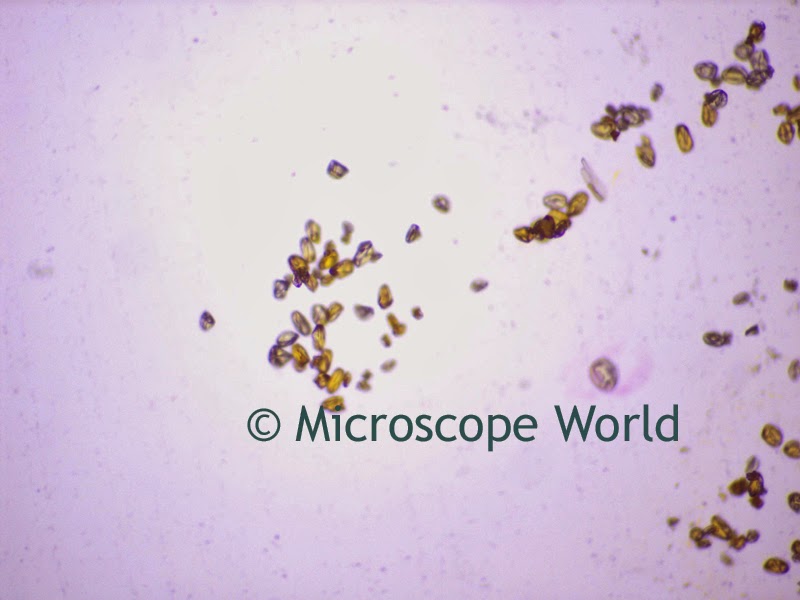
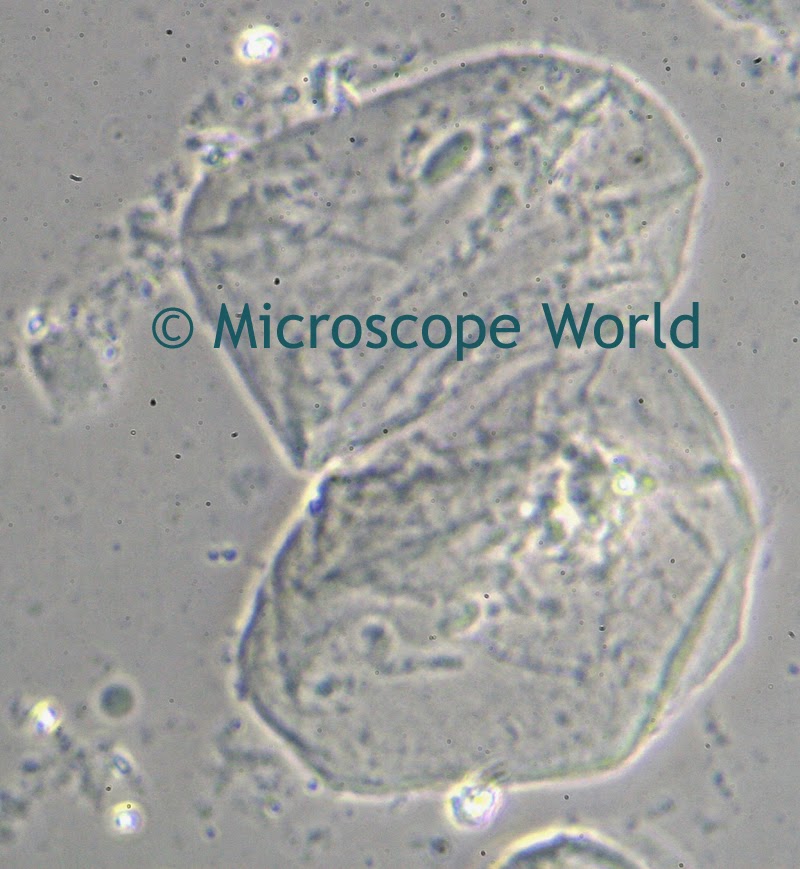
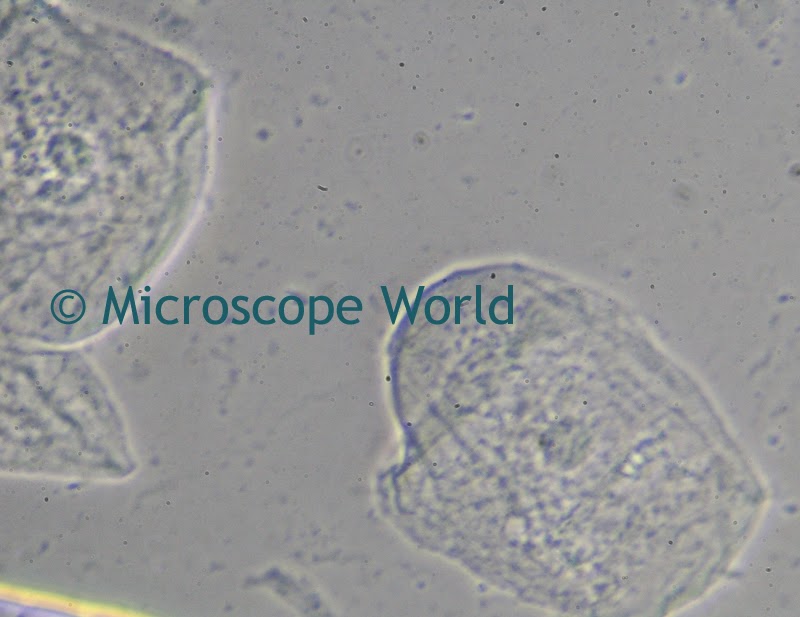
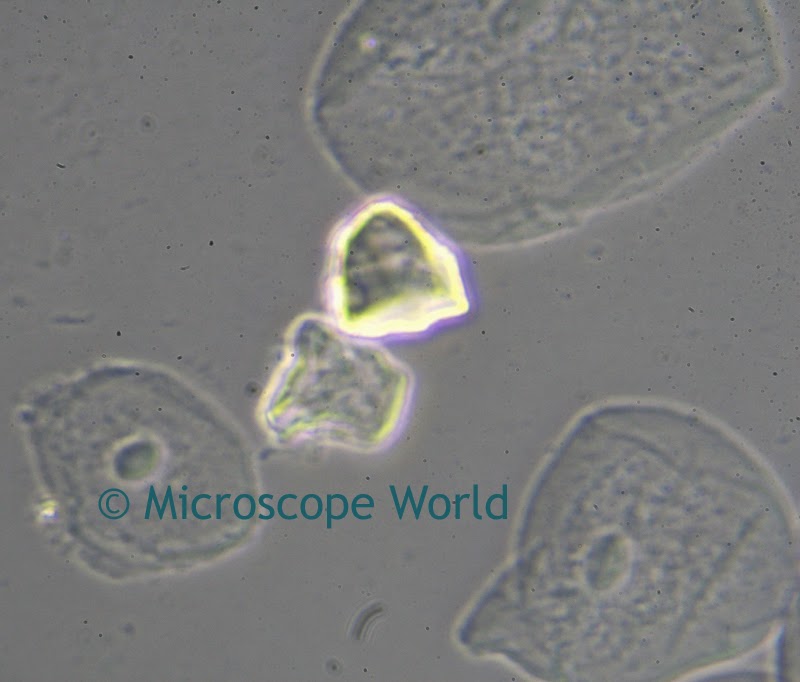
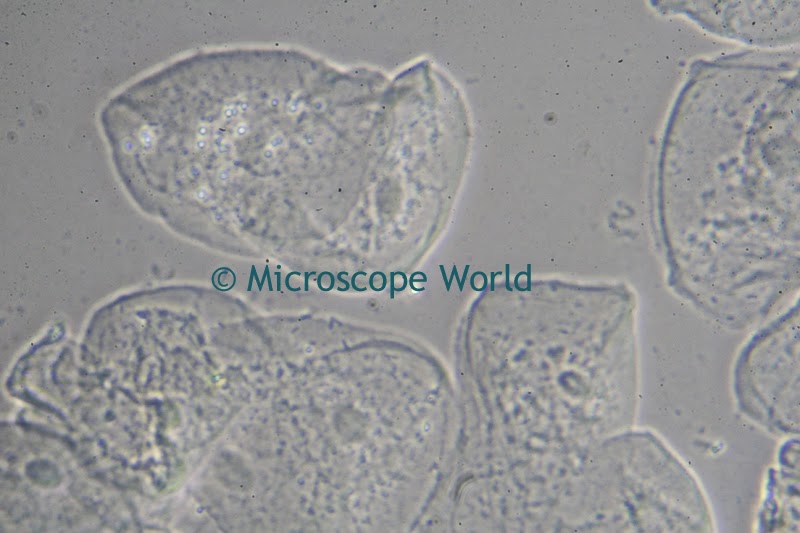
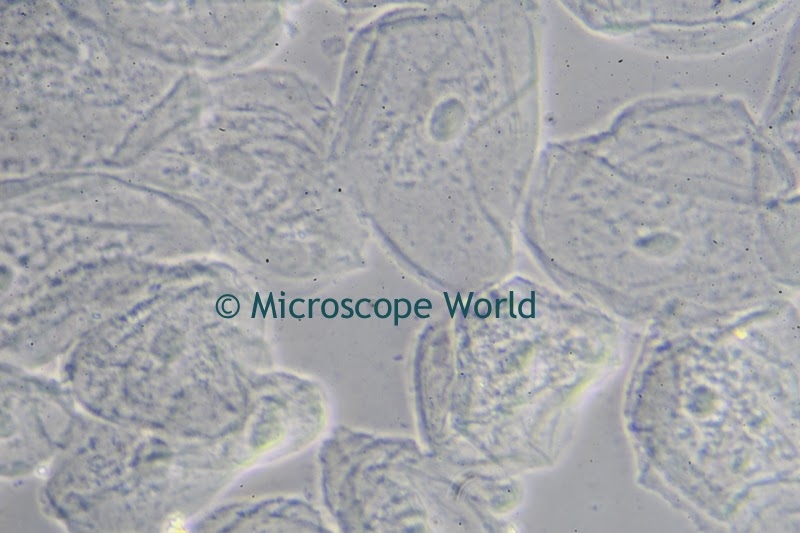
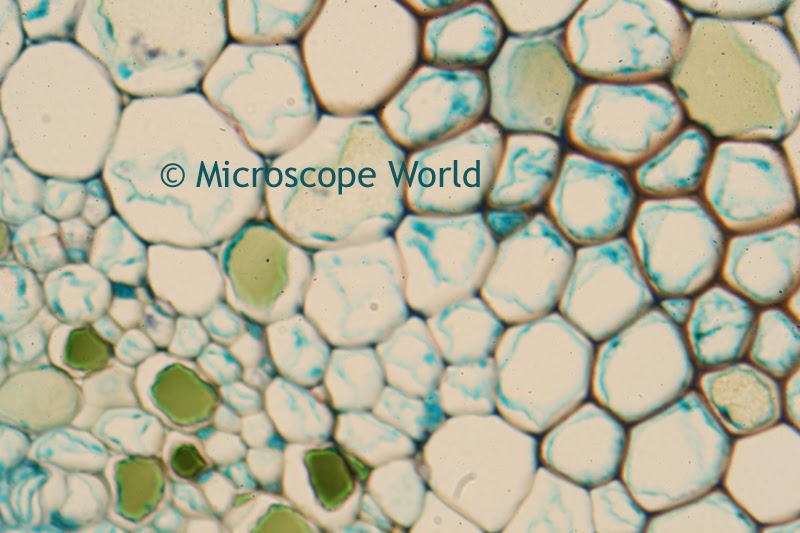
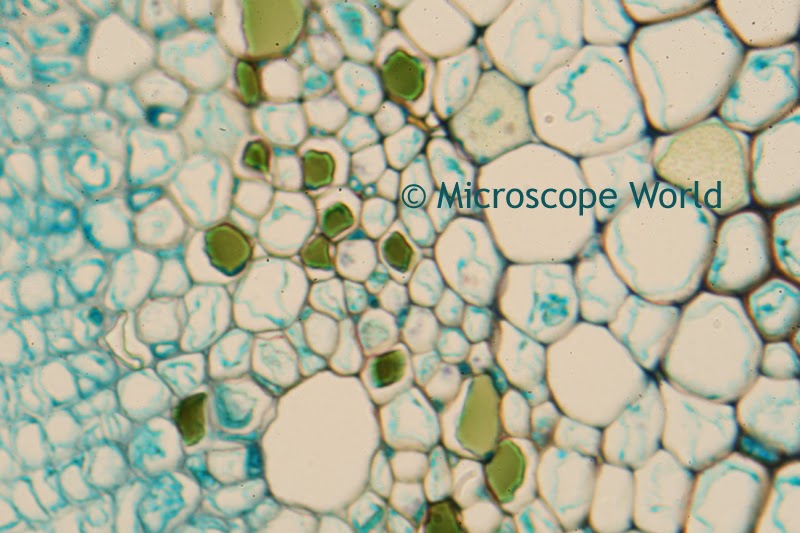
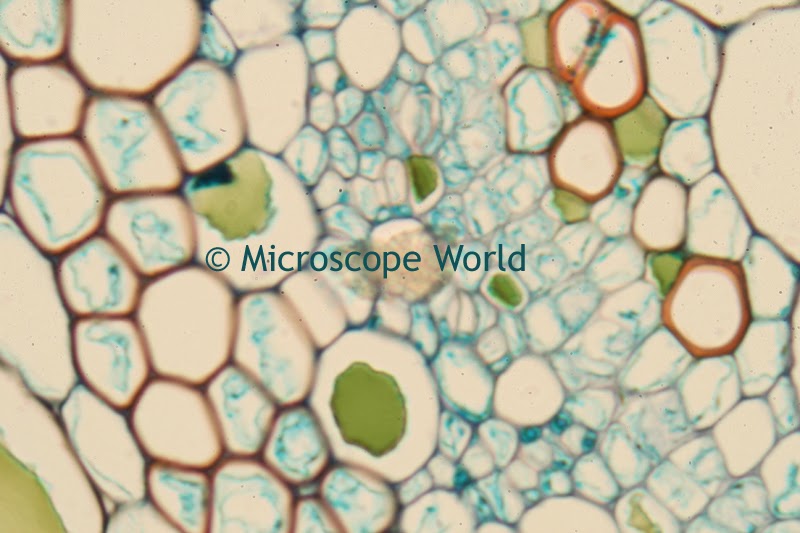
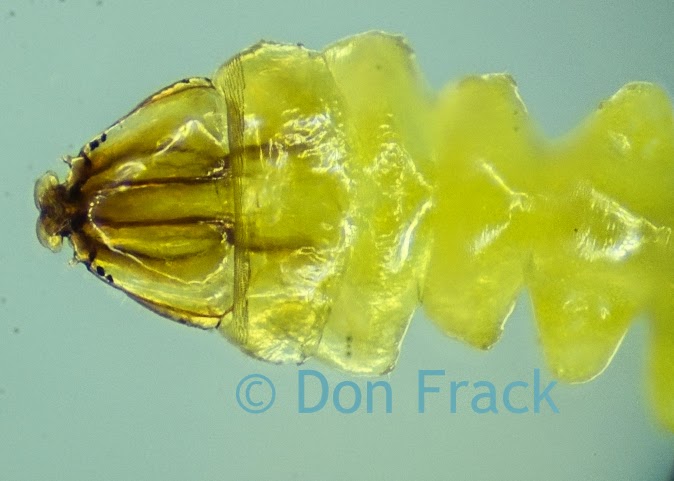
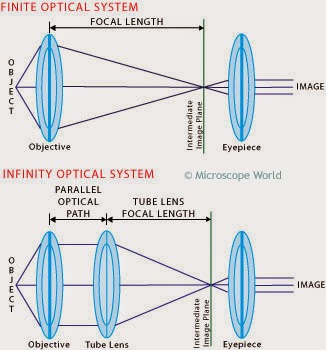
A customer of Microscope World's, Mr. Martin Moe, rears both Diadema and Tripneustes. This is a photo he captured of a Tripneustes Ventricosus Larvae at day 32 with posterior pedicellaria and cilia ridge just before settlement.
Tripneustes Ventricosus (commonly called the West Indian sea egg), is a species of sea urchin. These urchins are found commonly in the Caribbean Sea, Bahamas, and Florida at depths of less than 33 feet.
Tripneustes Ventricosus feeds on algae, but tends to avoid highly calcified coralline algae.
Tripneustes Ventricosus (commonly called the West Indian sea egg), is a species of sea urchin. These urchins are found commonly in the Caribbean Sea, Bahamas, and Florida at depths of less than 33 feet.
Tripneustes Ventricosus feeds on algae, but tends to avoid highly calcified coralline algae.
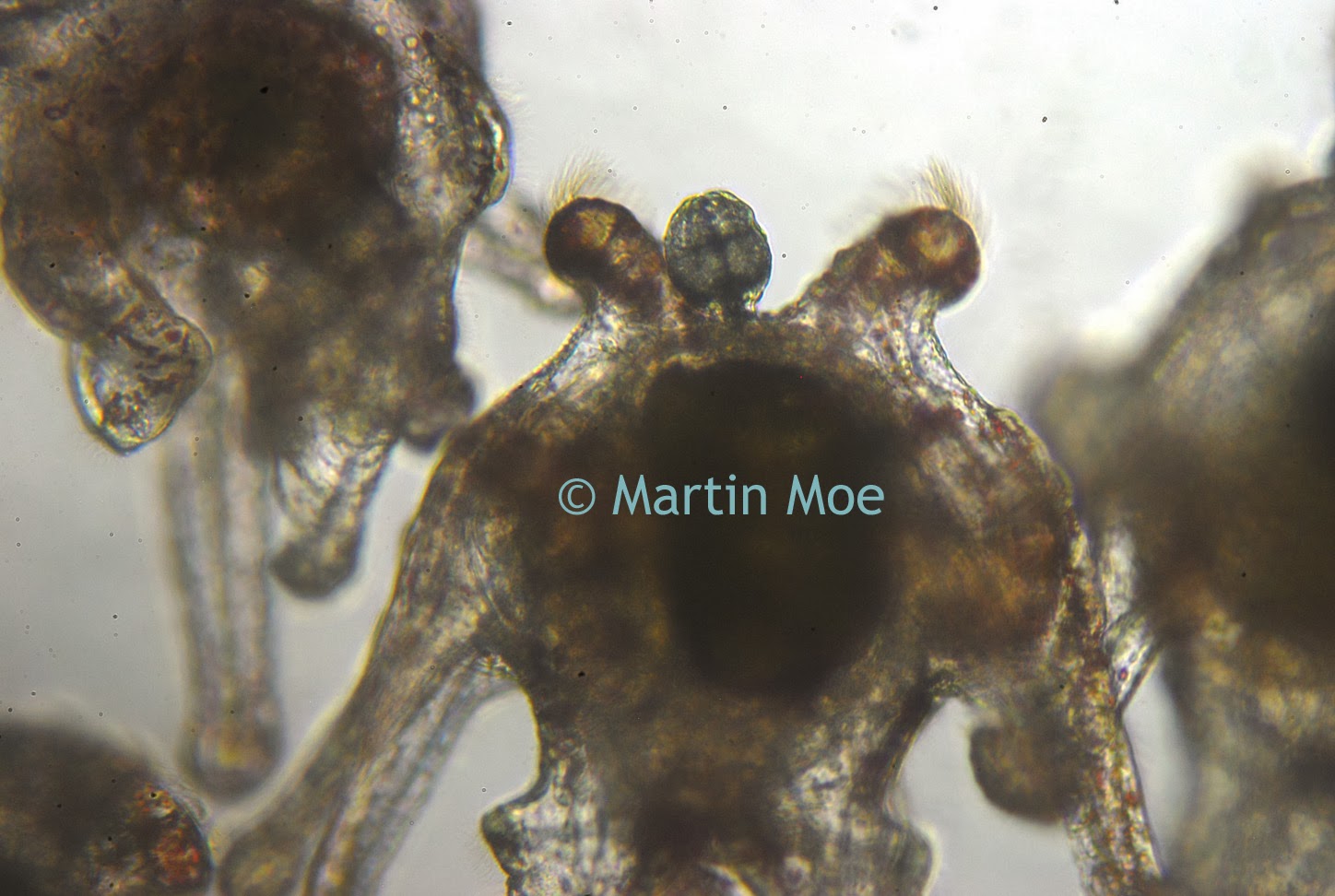 |
| Tripneustes Ventricosus - image courtesy of Martin Moe. |
The Tripneustes Ventricosus image above was captured using the Meiji MT4300 biological microscope.